Primary and Secondary Pollutants
Primary Pollutants
Primary pollutants are substances that produce pollution levels in the state in which they have been discharged at the source and are therefore considered to be harmful to human health and the environment.
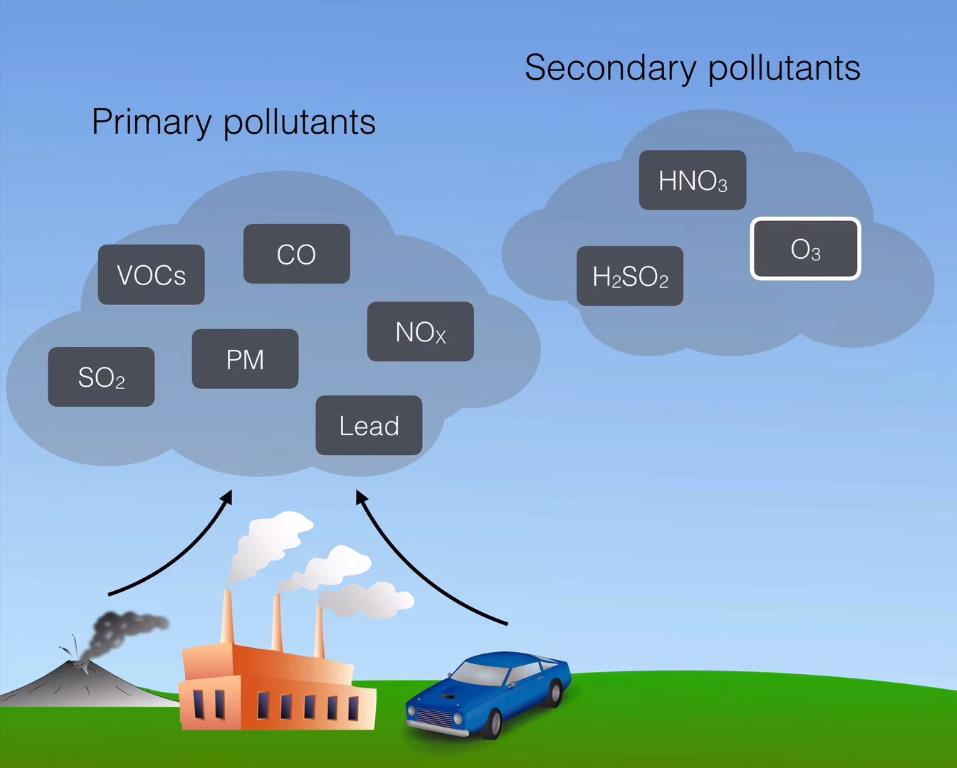
Primary pollutants pollute the environment because they are released directly into the ecosystem. It is possible that the substance discharged was previously present in certain amounts, but it is deemed the main pollutant if the extra release increases the overall physical quantity to levels that are considered harmful to human health.

Examples of primary pollutants include carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx, NO), Sulphur oxides (SOx), Sulphur dioxide (SO2), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and aerosols (dust, ash, salt particles).

Secondry Pollutants
Secondary pollutants that are formed due to interactions between primary air pollutants and other atmospheric components are called secondary pollutants. These interactions can be physical or chemical.
Examples of a secondary pollutant ozone, particulate matter, acid rain, Peroxyacyl nitrates (PANs), and other toxic chemicals.
Written By: Pooja Singh